Flash Translation Layer
In this page, we will explain how we design and implement Flash Translation Layer - FTL.
FTL provides abstract class, so you can implement your own FTL by inherit the class.
By default, we provide PageMapping, which implements Page-level FTL.

Components of Flash Translation Layer
Abstract Class
AbstractFTL class is defined in ftl/abstract_ftl.hh.
It defines six virtual functions (+ three virtual functions derived from StatObject).
initialize function handles warm-up procedure.
See PageMapping::initialize function for more details.
read, write, trim and format handles each I/O command.
getStatus function returns current mapping status.
This function exists for Identify Namespace of NVMe Interface.
Page-level FTL
We provides page-level mapping FTL, which defined as SimpleSSD::FTL::PageMapping in ftl/page_mapping.hh.
If you set [pal] SuperblockSize configuration, this FTL will work as superpage-level FTL.
PageMapping implements:
(Super) page-level address translation: See each I/O functions
Garbage collection: See
PageMapping::doGarbageCollectionWear-leveling: See
PageMapping::getFreeBlock
GC invoked when configured threshold is triggered (See PageMapping::writeInternal).
PageMapping::table stores LPN -> PPN mapping and FTL::Block stores block metadata and reverse mapping table.
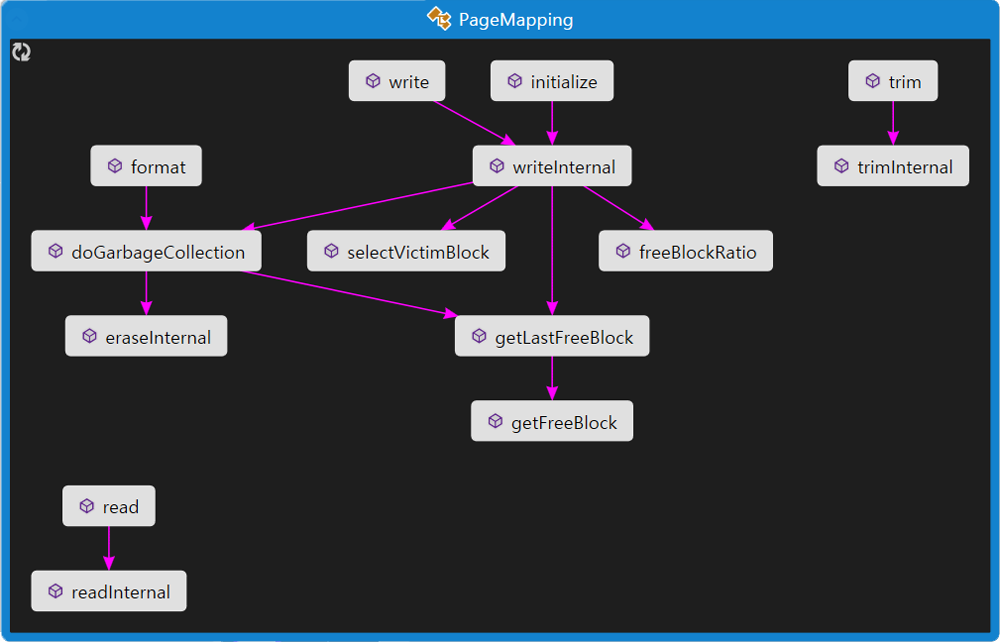
Function call diagram of PageMapping
Random I/O tweak
Commercial SSDs uses special algorithms to enhance random write performance. Instead of implementing such algorithms, SimpleSSD modified FTL for implementation convenience.
This tweak has same memory requirement with pure page-level FTL (without superpage configuration). It still uses superpage-level I/O for exploit internal parallelism, but also supports fine-granule (page-level) write handling.